Is all DMR equipment compatible?
Yes, and no; while basic functionality will work between systems (such as voice transmission) if your chosen manufacturer has performed interoperability testing, you might be using features outside those defined by the DMR standard. Before deciding what equipment to purchase, you should check what features you are currently using and find out if any are unique to your current equipment.
What frequency does DMR equipment work on?
Digital Mobile Radio works between the frequencies of 30 MHz (Megahertz) and 1000 MHz, also known as 1 GHz (Gigahertz). This range of DMR frequencies is divided into two categories:
1. Very High Frequency (VHF) - Range between 30 MHz and 300 MHz
2. Ultra High Frequency (UHF) - Range between 300 MHz and 1 GHz.
From these ranges, most DMR equipment falls into the 136 - 174 MHz and 403 - 527 MHz parts of the spectrum. Each country has its own organisation tasked with allocating licences, but some DMR frequencies are allocated as licence-free (for DMR Tier I) while others require a licence to operate.
Do I need a licence for DMR equipment?
The short answer is “it depends”. If you have a small number of users and basic communication requirements you may be happy to use DMR Tier I (see what are DMR tiers?) radios which do not require a license and are simple to use. It should be noted that Tier I equipment has a shorter range and are susceptible to interference from other users. If you require a more complex system you will need to apply for a licence from the frequency licencing body in your country.
What is the range of DMR?
The answer to this question depends on the equipment you are using and the infrastructure you have installed around it. As an example, the International Space Station, orbiting at an altitude of 408 km uses DMR to communicate with the earth, but there are very few obstructions between the station and the antennas on the ground so the signal is easily received. In comparison, a DMR Tier I radio operating inside a building may only work for around 100 metres.
DMR radio systems can have any range you wish them to have if the correct infrastructure is installed; DMR Repeaters can extend signals over a large area, but pockets of connectivity can be created by distributing data between repeaters through other means such as microwave links or the internet.
Talkpod extensive partner network means can we can pair you with a local expert to help you find the right system solution for your unique requirements. Contact us today to start your journey.
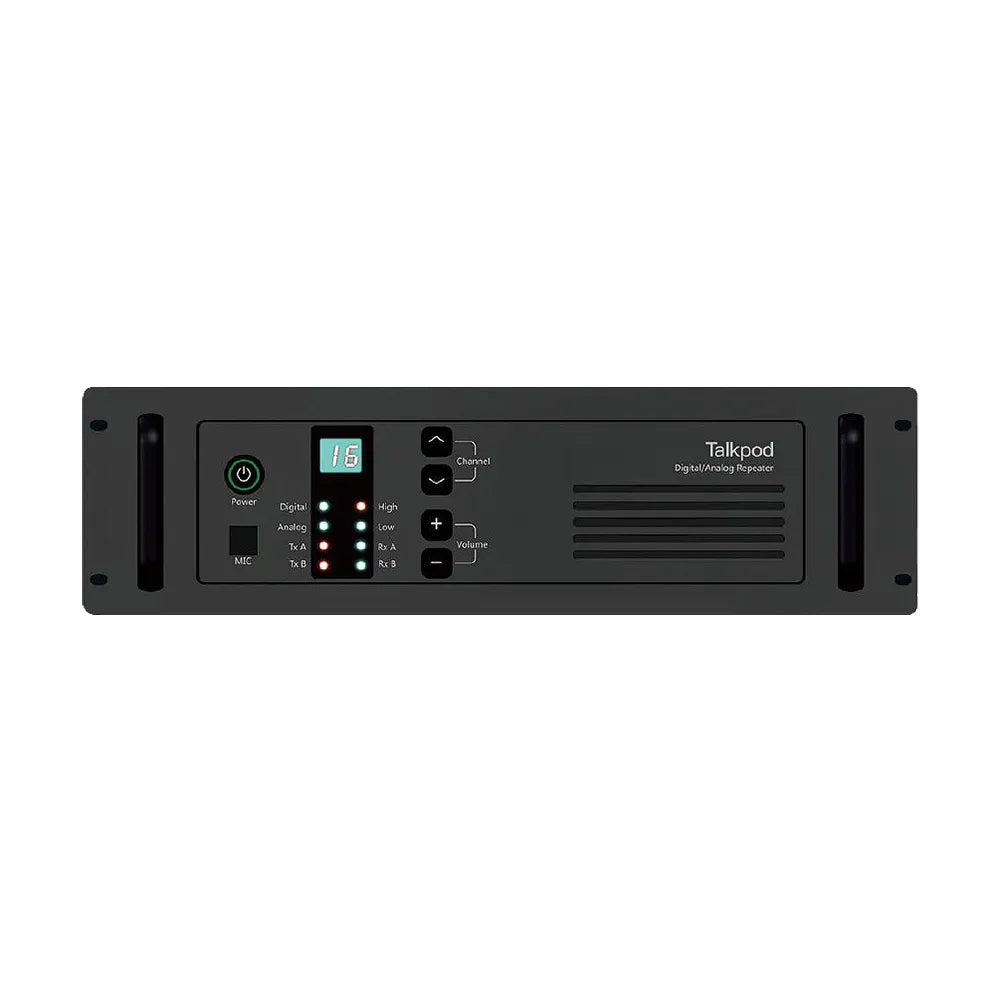
What is a DMR Repeater?
DMR radios are able to communicate with each other directly without a centralised system, but this is not always an ideal situation. Signals between radios connecting directly to each other can be hampered by obstructions in the line-of-sight between them such as trees, buildings, and hills.
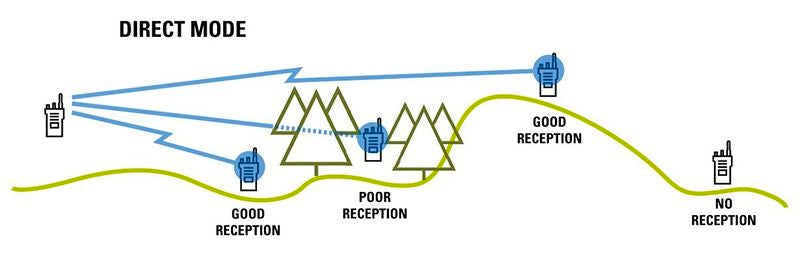
A DMR repeater added to the system allows radios to send their communications via a central point which repeats the message to the rest of the system. By installing a repeater high up (often on top of a building) the calls to the repeater are less affected by the obstructions. It also allows radios located far away from the repeater in opposite directions to communicate with each other, effectively increasing the range of the system.
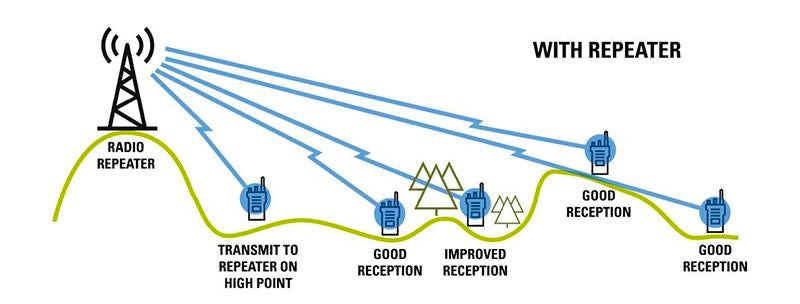
Repeater stations can be connected together by either retransmitting received signals (parroting) or by sending received signals to other repeaters on the system via other methods (internet, unidirectional transmitter, etc). With these methods, the range of the system is only limited by the amount of infrastructure you install.
Talkpod is a Members of the DMR Association?
Yes, Talkpod Technology Co., Ltd. is a Category 1 member – Full Members, Manufacturers of the Digital Mobile Radio Association since September 2016.
Talkpod Technology legally uses the DMR Trademark and works with all members of the Digital Mobile Radio Association to develop, promote and popularize DMR technology.

Has Talkpod obtained DMR’s patented technology authorization?
Yes, Talkpod's (Quanshun Group) DMR series products utilize patented technologies related to DMR and are officially authorized for use by the holders of DMR patents, with regular payment of DMR patent royalties.
Talkpod Technology is dedicated to innovation and respecting intellectual property rights. We believe in the importance of honoring and upholding the rights of patent holders, and we are committed to operating in full compliance with all applicable laws and regulations governing intellectual property.

Benefits of DMR Technology
As DMR is a fully public, open standard backed by a huge variety of suppliers. Through this users have both the security of supply and the advantages of continuous, competitive development. Open standards encourage wide ranging supplier participation; there are many examples of the successes of technologies developed in this way. The DMR standard scores highly against legacy analogue systems and other digital approaches.
Doubling of capacity in existing licensed channels
DMR enables a single 12.5 kHz channel to support two simultaneous and independent calls. This is achieved using TDMA, Time Division Multiple Access. Under TDMA DMR retains the 12.5 kHz channel width and divides it into two alternating timeslots A and B (illustrated in figure 1 below) where each timeslot acts as a separate communication path...
Backwards spectrum compatibility with legacy systems
License holders may need to keep hold of existing licenses to ensure backwards compatibility with their own legacy radios or with an external organisation’s analogue system. As DMR uses 12.5 kHz channels the required spectrum compatibility is built in. This is illustrated in figure 5 below.
Efficient use of infractructure equipment
With DMR TDMA you get two communications channels with one repeater, one antenna and a simple duplexer. Compared to FDMA solutions, two-slot TDMA allows you to achieve 6.25 kHz efficiency while minimising investments in repeaters and combining equipment. The required equipment of the two approaches for a simple system is shown in figure 6 below.
Longer battery life and greater power efficiency
Maximising battery life has always been one of the great challenges for mobile devices with limited options for increasing the talk time on a single charge. Since an individual call on two-slot TDMA only uses one of the two timeslots it requires only half of the transmitter’s capacity. The transmitter is idle half of the time; whenever it’s the unused timeslot’s “turn”. By cutting the effective transmit time in half...
Encryption
Although DMR was primarily developed for civil and industrial applications the protection of the confidentiality of the exchanged information can be important.
The DMR Association has defined the following options for traffic encryption:
ARC4 40 bit, DES 64 bit, AES128 128 bit, AES256 256 bit...
Location Information Protocol
There is a standardized option for the transmission of position information from DMR radios over the network. The LIP protocol it-self has been taken from ETSI-TETRA, it allows for the transmission of localization data in an interoperable format and for the Over the Air configuration / modifications of triggers.
The DMR radio will transmit its ...
Ease of use and creation of data applications
The end-to-end digital nature of DMR means that applications such as text messaging, GPS and telemetry can be easily added onto radio devices and systems. The DMR standard supports the transmission of IP data over the air enabling the easy development of standard applications.
The doubling of channel capacity that DMR implementations achieve is also key to adding data ...
System flexibility through simultaneous use of TDMA channels
While voice is using the first time slot then the second time-slot can, in a TDMA system, be used for transmitting application data such as text messaging or location data in parallel. This is useful, for example, in dispatch systems that provide both verbal and visual dispatch instructions. This is enhanced data capability is becoming increasingly important in data rich environments...
Advanced control features
The DMR standard allows for the ability to use the second time-slot for reverse-channel signalling – that is, instructions in the form of signalling being sent to the radio on the second time slot channel while the first channel is in a call. This enables priority call control, remote control of the transmitting radio, or emergency call pre-emption and gives precise control and flexibility to the operator of a radio system...
Superior audio performance
DMR digital technology provides better noise rejection and preserves voice quality over a greater range than analogue, especially at the farthest edges of the transmission range. This is because a great deal of effort was put into selecting Forward Error Correction (FEC) and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) coders when developing the standard. With these coders receiving radios detect and ...
Direct Mode
This mode of communications provides mobile users with the ability to communicate directly from radio to radio when out of range of the network.
DMR offers two possibilities for DMO:
Normal DMO - One communication on a 12,5 kHz channel
Frequency efficient DMO - Two independent communications on a 12,5 kHz channel using both TDMA time slots.
Green Technology
Optimal efficiency was a key objective in designing DMR. This applies not only to performance, equipment cost and ease of implementation but also to energy efficiency.
4 Level FSK modulation
Constant envelope modulation allows the use of non-linear high efficiency power amplifiers...
Explore DMR from Talkpod Technologies
Equip your teams with ultra-thin portables and extra-tough mobiles, industry-leading data applications and flawless system scalability.
Our devices are designed to the highest specifications both inside and out. With outstanding range, battery life, and responsiveness, your team can collaborate more effectively, work more efficiently, and create more loyal customers.
Portables
Connect your entire operation with Talkpod digital portable radios.
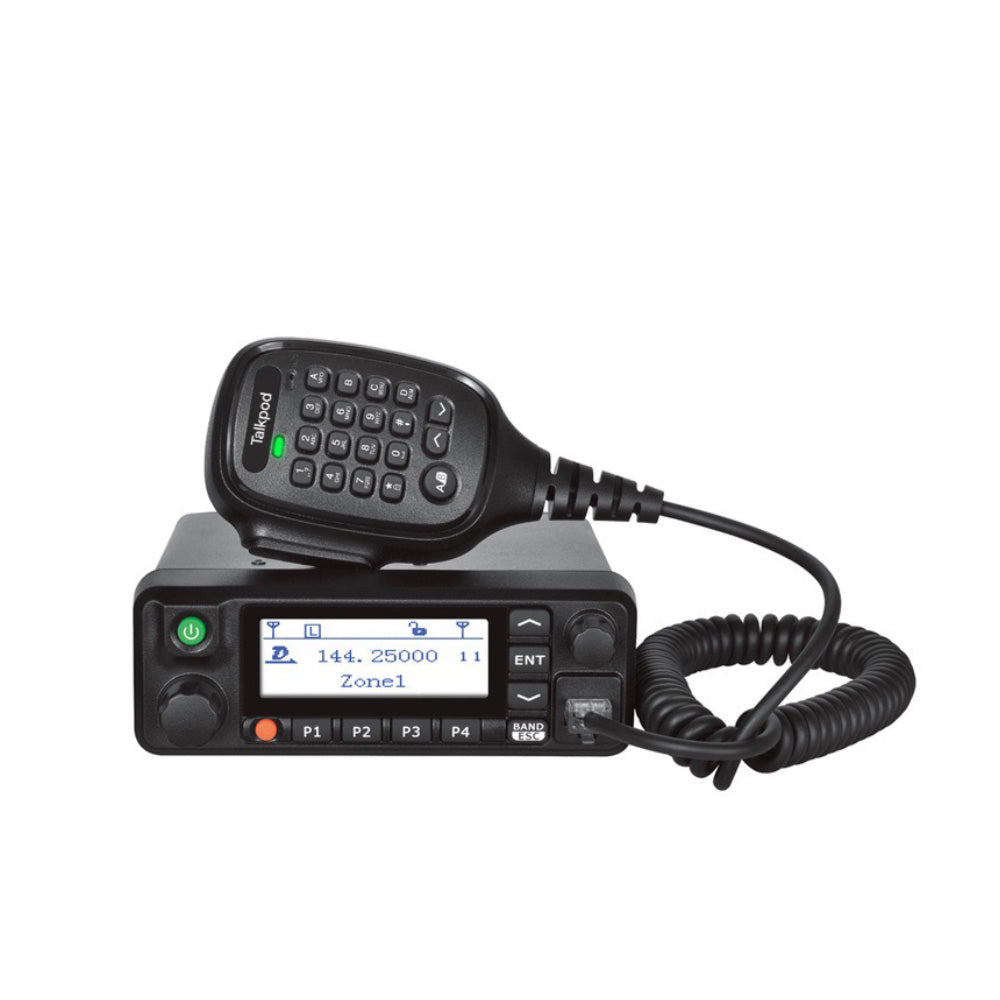
Mobiles
Keep your teams connected with Talkpod mobile radios.
Repeaters
Talkpod reapeater systems are designed to scale with your organization, so you can grow as large as you like.
Talkpod DMR Series
DMR Wiki:

DMR: The Backbone of Resilient First Responder Communications
In the demanding world of first responder operations, where natural disasters and catastrophic events frequently disrupt conventional telecommunication services, the need for a resilient communicat...

Revolutionizing Field Testing: The Criticality of DMR Tier 3 Radio Assessments
In the realm of Land Mobile Radio (LMR) protocols, Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) Tier 3 stands out for its rapid adoption across various sectors, including utilities, government agencies, and commerci...

In the realm of radio communication, the Individual Call stands out as a tailored, direct method of reaching out to a specific user. This blog post delves into the essence of Individua...

In the world of radio communications, the term 'ID' refers to an identity or numeric identifier that plays a crucial role in distinguishing one user or device from another. This blog post explores...

Group calls are an essential feature in two-way radio systems, allowing a single user to communicate with multiple members simultaneously. This blog explores the concept of group call, its signifi...

In the realm of digital communication, the term "full-duplex" signifies the capability of a system to transmit and receive data simultaneously. Imagine having a conversation over the p...
Need to contact a partner?
Get help to solve a complex business challenge or pursue purchasing.