Understanding Push-to-Talk over Cellular (PoC) Push-to-Talk over Cellular (PoC) is a service that utilizes 4G and LTE networks to provide wide-area group communication. This system leverages the cellular infrastructure, offering extensive coverage beyond the limitations of traditional radio network repeaters and base stations.
Originating with Nextel in 1987, PoC transformed business communication by transmitting small voice packets over its iDEN network, marking a shift from the conventional two-way radio systems. Despite Nextel's integration into Sprint and the eventual shutdown of the iDEN network, PoC has evolved to integrate the functionalities of narrowband digital radios and broadband networks, supporting features like messaging, group calls, GPS tracking, and emergency alerts.
How PoC Functions Also known as Radio over IP (RoIP), PoC works similarly to VoIP but with handheld devices accessing cloud-based services for multimedia communication. These devices, equipped with SIM cards, connect to the internet through cellular networks provided by carriers such as AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon, as well as through Wi-Fi, embodying the characteristics of IoT devices.
At its core, PoC uses cloud-hosted controllers operated by service providers or privately by users, facilitating seamless connectivity and communication over extensive areas. The integration of Android apps in PoC devices further simplifies access to these comprehensive communication services.
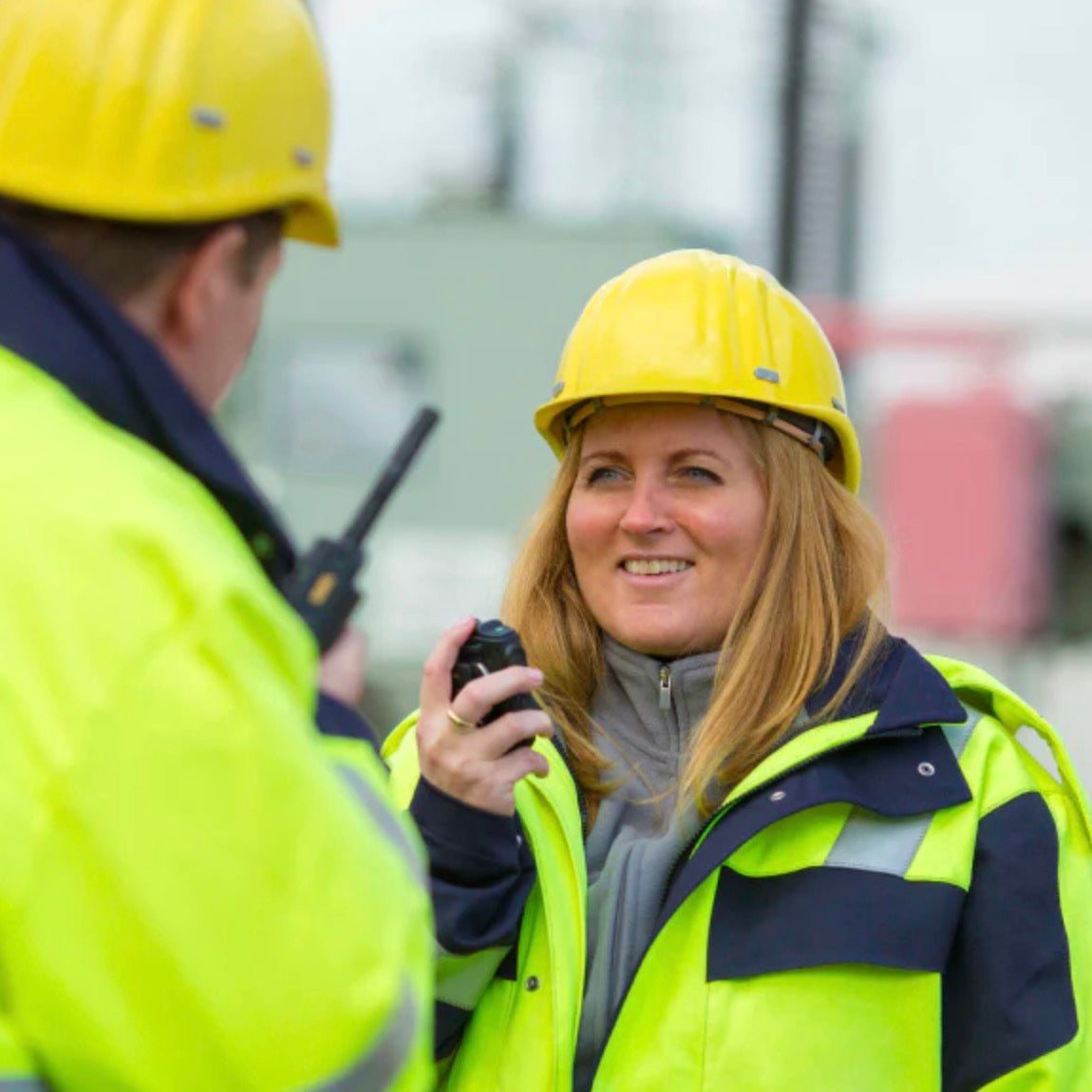
Group Calling with PoC Mimicking the instant group call feature of traditional radios, PoC enables users to communicate with multiple members simultaneously, facilitated by a PTT button or dispatch applications. This capability is organized through call groups, defined by roles, locations, or project types, allowing for flexible and efficient coordination across various sectors.
In summary, PoC represents a significant advancement in communication technology, merging the reliability of two-way radios with the extensive reach and advanced capabilities of modern cellular networks, thus offering a robust solution for today's dynamic communication needs.